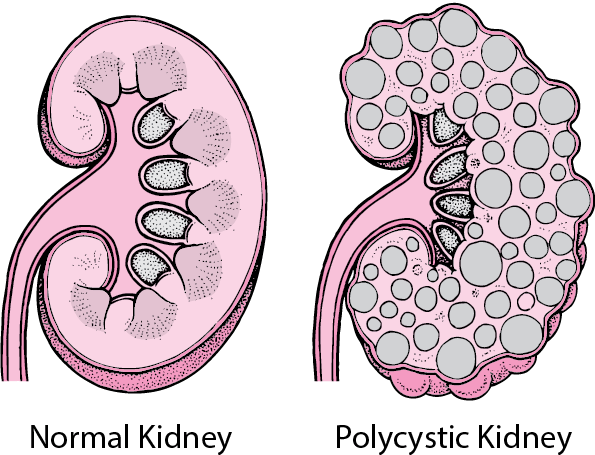
Terms in this set 14 polycystic kidney disease PKD genetic disorder characterized by growth of cysts which can replace the mass of the kidney and lead to renal failure. -defective ECM formation allows cyst formation vascular aneurysms.
Quick Facts Polycystic Kidney Disease Pkd Merck Manuals Consumer Version
Headaches Hematuria blood in the urine High blood pressure Pain in the back or sides Frequent urinary tract infections UTIs Unexplained abdominal swelling.

. If PKD affects the brain it can cause an aneurysm. What are the signs and symptoms of PKD. People with PKD may have cysts in their liver pancreas spleen ovaries and large bowel.
Cysts in the liver can also occur with PKD. These cysts may begin to develop in utero in infancy in childhood or in adulthood. The following symptoms may indicate that you need to be examined and possibly diagnosed and treated for polycystic kidney disease.
It may come and go or be persistent. ARPKD is primarily caused by mutations in polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 PKHD1 which encodes fibrocystin also known as polyductin a protein that localizes to the primary cilium and basal body. It causes fluid-filled cysts to form in the kidneys.
20 Which of the following may indicate polycystic kidney disease. PKD cysts cause high blood pressure and problems with blood vessels in the brain and heart. PKD can affect other organs besides the kidney.
Autosomal Dominant PKD Autosomal dominant PKD is often not diagnosed until later in adulthood. The cysts vary in size and they can grow very large. Potassium calcium and phosphorus need no special attention.
These cysts may begin to develop in utero in infancy in childhood or in adulthood. People affected by the most common form of polycystic kidney disease autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease experience the following symptoms. A a urinary infection B phenylketonuria C.
PKD can also affect the brain or heart. Manifestations of the disease include hepatic fibrosis and greatly enlarged kidneys and cysts typically affect the collecting ducts. Polycystic kidney disease is a disorder that affects the kidneys and other organs.
Cysts in these organs usually do not cause serious problems but can in some people. The signs and symptoms of ADPKD such as pain high blood pressure and kidney failure are also PKD complications. During an ultrasound a wandlike device called a transducer is placed on your body.
Pressure on renal blood vessels obstructs perfusion leading to tissue degeneration and obstructed tubular flow. Polycystic kidney disease PKD is an inherited disorder in which clusters of cysts develop primarily within your kidneys causing your kidneys to enlarge and lose function over time. PKD may impair kidney.
It emits sound waves that are reflected back to the transducer like sonar. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease can also cause urinary tract infections blood in the urine hematuria. Cyst-affected nephrons are interspersed with normal unaffected nephrons.
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease The two most common symptoms are headaches and pain in the back and the sides between the ribs and hips. Having many cysts or large cysts can. The majority of individuals with ARPKD present in the neonatal period with enlarged echogenic kidneys.
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD 2 is one of the most common monogenic diseases affecting 1 in 8001000 people worldwide and is the fourth-leading cause of end-stage renal failure 1 2ADPKD is caused primarily by mutations in PKD1 or PKD2 The typical renal phenotype of ADPKD is the insidious development of. Cysts are noncancerous round sacs containing fluid. Polycystic kidney disease PKD is an inherited kidney disorder.
- Clients with polycystic kidney disease waste sodium rather than retain it and therefore require an increase in sodium and water in the diet. A nurse is caring for a hospitalized client with polycystic kidney disease who has intravenous pyelography IVP. Cysts are non-functioning tubules filled with fluid.
Polycystic kidney disease PKD or PCKD also known as polycystic kidney syndrome is a genetic disorder in which the renal tubules become structurally abnormal resulting in the development and growth of multiple cysts within the kidney. Polycystic kidney disease a hereditary genetic disease characterized by formation of fluid-filled cysts and massive kidney enlargement affects both children and adults polycystic kidney disease has two forms autosomal dominant is relatively common and primarily affects adults autosomal recessive is rare and is present at birth affecting children. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease ARPKD historically called infantile PKD is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in neonates infants and young adults.
For polycystic kidney disease certain tests can detect the size and number of kidney cysts you have and evaluate the amount of healthy kidney tissue including. Other symptoms of PKD flank pain headaches nausea anorexia UTI liver and pancreatic cysts cardiac valvular disease hypertension renal calculi cerebral aneurysms diverticular disease negative impact as renal function worsens accumulation of nitrogenous wastes altered fluidelectrolyte balance impaired function in multiple organ. Polycystic kidney disease PKD or PCKD also known as polycystic kidney syndrome is a genetic disorder in which the renal tubules become structurally abnormal resulting in the development and growth of multiple cysts within the kidney.
A anuria B oliguria C proteinuria D hematuria E ketonuria 21 Abnormally high levels of glucose in the urine may indicate __________. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD historically referred to as adult PKD is increasingly recognized as a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in children and young adults. Etiology of autosomal dominant PKD ADPKD -PKD1 and PKD2 genes code for polycystin proteins.
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease ARPKD belongs to a group of congenitalhepatorenal fibrocystic syndromes and is a cause of significant renal and liver-related morbidity and mortality in children. In many cases ADPKD does not cause signs or symptoms until your kidney cysts are a half inch or larger in size. Clusters of fluid-filled sacs called cysts develop in the kidneys and interfere with their ability to filter waste products from the blood.
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder that causes many cysts to grow in the kidneys. Pathophysiology of Polycystic Kidney Disease cysts of increasing size and number replace the functional tissue leading to end-stage renal disease. The pain may be mild or severe.
The growth of cysts causes the kidneys to become enlarged and can lead to kidney failure. Blood in the urine Headaches High blood pressure Kidney stones and infections Pain in the back or side Swelling of the abdomen and feeling full Urinary tract infections Diagnosis.

Polycystic Kidney Disease Middlesex Health

Polycystic Kidney Disease Pkd Causes Treatment Gleneagles Hospital

/polycystic-kidney-disease-signs-symptoms-and-complications-5204728-Final-44f1e1e2faaf4c5a937146f13dc9d938.jpg)
0 Comments